95% of cybersecurity incidents can be traced back to human error, emphasizing the critical role of employee awareness and training in preventing cyberattacks.
Most breaches still start with people, not firewalls. Effective, ongoing Security Awareness Training—paired with phishing simulations and simple controls like MFA—cuts risk, proves compliance (PIPEDA/Law 25), and turns your team into a real security layer. The payoff: fewer incidents, faster reporting, and lower breach costs. Verizon’s DBIR finds the human element is present in ~68% of breaches—so this is where ROI lives.
Attackers exploit psychology, urgency, curiosity, trust, not just technology. A rushed “CEO” text, a realistic invoice, a deepfake voicemail: one distracted click can bypass expensive tools. Hybrid work amplifies this risk. Staff jump between email, Teams/Slack, and finance apps from home networks and mobile devices. Training meets them where they work. Short, monthly lessons build habits; phishing simulations make those habits automatic.
For Canadian SMBs, the business case is clear. Regulators expect reasonable safeguards, and documented training demonstrates due diligence under PIPEDA and Québec’s Law 25. That means role-based content for finance, HR, and executives; realistic scenarios tied to Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and QuickBooks; and simple rules like two-person verification for payment changes.
Culture is the multiplier. Reward fast reporting, not perfection. Give employees a one-click “report phish” button and a no-blame policy. Then measure what matters: phish-prone rate, report rate, and time-to-report. When leaders model the behaviour and MFA covers crown-jewel systems, people stop being the weakest link and become a responsive, resilient control—one that pays for itself by preventing a single wire fraud, ransomware entry, or privacy incident.

Why Is Security Awareness Training Important?
Reducing Human Error:
Cybercriminals frequently exploit human mistakes. Consequently, security awareness training minimises these errors by educating employees on how to spot threats and take appropriate actions. Most risky moments are small: a hurried click on a link, approving an MFA prompt you didn’t initiate, sending a file to the wrong “Paul” in Outlook’s auto-complete. Good training gives people simple, repeatable heuristics—like TIP (Tone, Identity, Path)—to slow down and verify before acting. It should be role-based (finance sees Business Email Compromise scenarios; executives practise approval spoofing and deepfakes) and reinforced with micro-lessons right after risky behaviour.
Over time, this builds “muscle memory” so staff recognise tells (odd language, mismatched domains, urgent payment requests) and respond correctly. Measure improvement with practical KPIs such as phish-prone rate, report rate, and time-to-report; aim for steady month-over-month reductions rather than perfection on day one.
Phishing Simulations:
Moreover, training programs often include phishing simulations—realistic exercises that test employees’ abilities to recognise phishing attempts. These simulations help employees understand how sophisticated these attacks can be and how to avoid falling victim. Treat simulations like fire drills: frequent, safe-to-fail, and progressively harder. Start with generic lures (shipping, HR updates) and move to spear-phishing, QR-code (“quishing”), MFA fatigue, SMS (smishing), and voice (vishing/deepfake) scenarios.
Always include a one-click “Report Phish” button so success isn’t just “not clicking,” it’s reporting quickly. Deliver instant, bite-size coaching when someone interacts with a simulation—no shaming, just clear guidance. Track who reported first, celebrate “top reporters,” and feed real reported phish back into the simulation library so your drills mirror what attackers actually try against your business.
Fostering a Culture of Security:
When all employees understand the importance of cybersecurity, they become more vigilant and proactive. As a result, they create a culture of security within your organisation. Everyone, from leadership to new hires, plays a role in keeping the company safe. Culture shows up in daily habits: leaders publicly take the training, managers praise fast reporting, and teams follow a simple two-person verification rule for any payment or banking change. Bake security touchpoints into onboarding, quarterly town halls, and Slack/Teams nudges.
Create a network of “security champions” across departments to spot risky workflows and share fixes. Most importantly, adopt a no-blame policy for near-misses; the sooner people feel safe raising a hand, the faster you contain real threats. Over time, you’ll notice fewer urgent escalations, clearer handoffs to IT/MSSP, and tighter alignment between business goals and security controls.
Ensuring Compliance:
Additionally, many regulations, such as PIPEDA and Law 25, expect businesses to provide regular security and privacy training to employees. Fulfilling these requirements not only supports compliance but also enhances overall security. Maintain an audit-ready training matrix, attendance logs, quiz results, and policy acknowledgements (acceptable use, email/record retention, privacy). Map modules to privacy topics (personal information, consent, breach reporting) and keep artefacts for your compliance file.
This documentation helps with customer due diligence, insurance underwriting, and RFP responses, signalling that you operate with disciplined safeguards. Pair training with clear procedures—incident reporting, vendor/payment verification, and data handling—so regulators and partners see a coherent system, not isolated activities. In short, awareness training is both a risk reducer and a compliance enabler that strengthens trust with clients, boards, and insurers.
The biggest people risks
Phishing & Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Phishing and BEC remain the fastest way into a business because they exploit people, not systems. Fake invoices, payroll changes, “CEO” wire requests, QR-code (“quishing”) links, SMS delivery texts, and MFA fatigue prompts all aim to rush a decision. Reduce this risk by disabling legacy email protocols (IMAP/POP/SMTP AUTH), enforcing MFA on email and SSO, and running monthly phishing simulations that mirror the tools your teams actually use—Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, QuickBooks, and common shippers. Add two-person, out-of-band verification for any banking change and implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC (reject) to curb spoofing. Reinforce these practices with guidance from the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security in your regular comms.
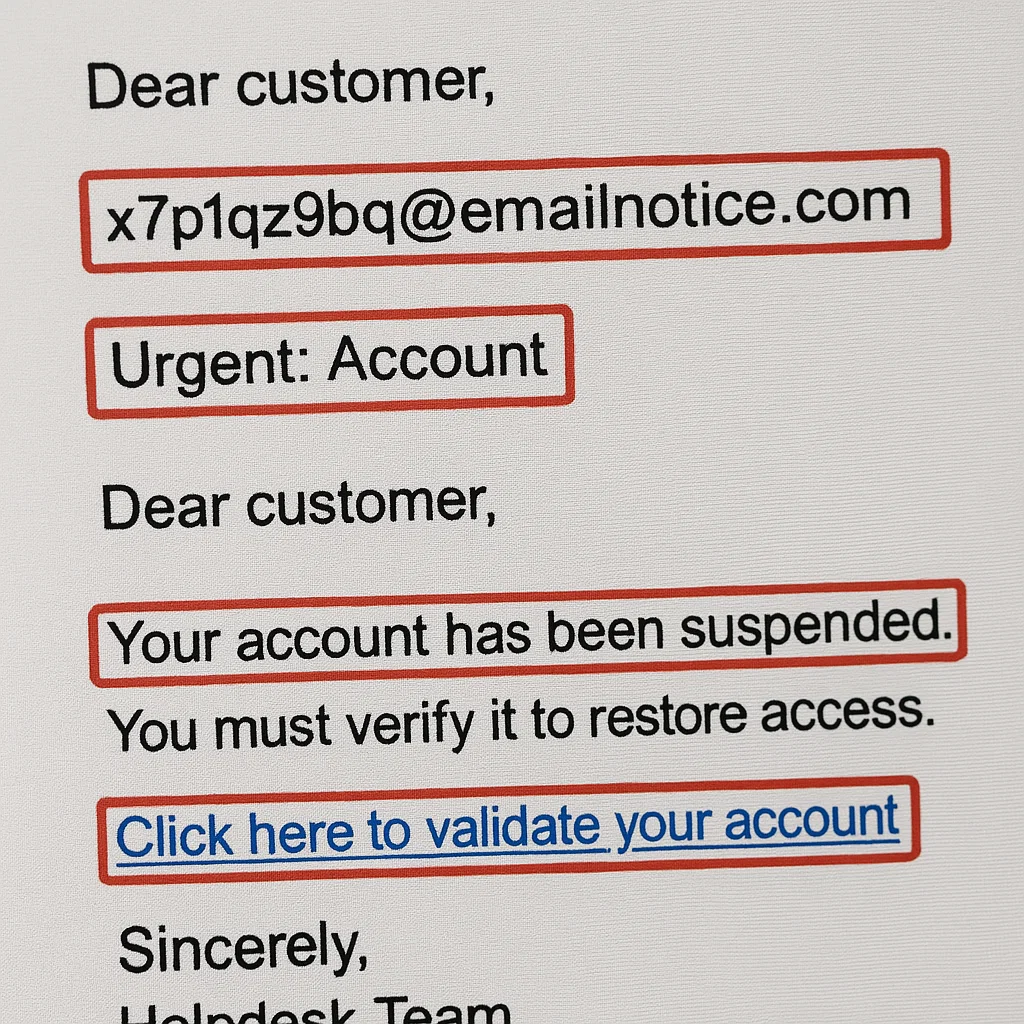
Weak or reused passwords
Password reuse turns one breach anywhere into access everywhere. Roll out a company-wide password manager so teams can store and share credentials safely, and push as much access as possible through SSO to shrink the number of standing passwords. Keep MFA “on” for everything that matters—email, finance, remote access—and insist on unique, long passphrases for the few accounts that still need passwords. Screen new passwords against known breach lists and prioritise phishing-resistant options (FIDO2/passkeys) for finance and admin roles.
Oversharing & social engineering
Attackers love public breadcrumbs—org charts, OOO notices, supplier lists—because they fuel convincing pretexts. Coach staff to verify out-of-band every time: call a known number or use a saved contact, never the one in an email. Publish a one-page “How we approve payments” policy and pin it in Teams/Slack so no one guesses under pressure. Trim unnecessary staff details on your website, delay posts about sensitive projects or travel, and train reception/admin teams to handle unexpected visitors, couriers, and mystery USB sticks without plugging anything in.
Slow or silent incident reporting
Minutes matter. When people hesitate, attackers persist. Make reporting a reflex with a simple three-step rule: Stop → Screenshot → Report to your MSP/MSSP. Add a one-click “Report Phish” button in Outlook/Gmail, publish 24/7 contacts, and print escalation steps where people can see them. Adopt a no-blame approach and reward speed and signal over perfection. Track time-to-first-report and celebrate top reporters each month to reinforce the behaviour you want.
Bonus risks you can tame quickly
Clamp down on shadow IT and risky browser extensions by approving a small, safe app catalogue. Protect against lost or stolen devices with full-disk encryption, remote wipe, and auto-lock after five minutes. Cut email misdirects by turning on external-recipient warnings and a two-minute send delay so people can catch mistakes before they leave the building.
Evidence-Based Training

- “Good” training feels light on time, heavy on impact. The cadence is short and predictable—10–12 minute modules each month with a quarterly live refresher—so people can complete it between meetings without fatigue. Add gentle nudges in Teams/Slack and a 90-second recap video for those who prefer to watch. A simple rhythm (learn → practice → report) keeps attention high and makes new habits stick.
- Content is role-based and mapped to real business risk. Finance practises Business Email Compromise (BEC) and vendor-banking changes; HR handles privacy, PI/PII (personally identifiable information), and document sharing; executives rehearse deepfake voice approvals and travel scenarios; IT focuses on secure admin hygiene and privileged access. Tie each module back to your “crown-jewel” processes—payroll, receivables, client data—so relevance is obvious.
- Simulations are realistic and multi-channel. Phishing templates mirror your actual stack (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, QuickBooks, shipping carriers) and include modern lures: QR-code “quishing,” SMS “smishing,” OAuth consent prompts, MFA fatigue, and voicemail “vishing.” Time a few drills to business cycles (month-end, year-end, busy season) so staff practise under real pressure. Rotate in vendor-impersonation scenarios that attackers love.
- Just-in-time coaching is where behaviour changes. If someone clicks, they land on a micro-lesson that highlights the missed cues (sender domain, tone, link path) and gives a simple next step: report, reset password, or call finance. Repeat clickers get a supportive manager check-in, not public shaming—psychological safety drives faster reporting.
- Measure what matters with clear KPIs. Establish a baseline and track phish-prone rate, report-rate, time-to-report, repeat-clicker reduction, and policy acknowledgement. Segment by department and role; aim for PPR trending below 5%, report-rate above 60%, and first reports within 10 minutes for high-risk roles. Share a one-page dashboard with leadership monthly.
- Close the loop operationally. Every reported phish is triaged, tagged, and fed into your SIEM/SOAR or routed to your MSSP; detections and mail-flow rules are updated, and lessons re-enter the simulation library. Finish with compliance-ready records—attendance, scores, sign-offs, and a training matrix mapped to PIPEDA and Law 25 topics—plus versioned policies, data-residency notes, and onboarding/offboarding tracking. Add accessibility (captions, readable fonts) and bilingual options to maximise uptake, and recognise “top reporters” each month to keep the culture positive and engaged.
Metrics that show real risk reduction
- Phish-prone rate (PPR). Define it clearly: PPR = (clicks + credential submits) ÷ total recipients for a given simulation. Track it monthly and by department/role. Set expectations early—finance and executive assistants often start higher. Your goal is a steady down-trend to <5% by months 6–9. Use control charts to see signal vs. noise and annotate spikes with context (e.g., quarter-end spoof theme).
- Report-rate. Measure reports ÷ total recipients (or ÷ total openers for a stricter view). High report-rates are protective even when some people still click. Target >60%, then push toward 70–80% in high-risk teams. Publish a monthly “first-reporter” shout-out and track false-positive rate to keep the bar realistic. Pair the metric with enablement—one-click report buttons and clear “what happens next” feedback.
- Time-to-report. Capture minutes from send to first valid report (median and 90th percentile). Faster signals shorten attacker dwell time and reduce downstream losses (wire fraud, ransomware). Set SLAs by role: <10 minutes for finance and EAs, <20 for everyone else. Use automation to notify responders, open tickets, and push indicators to email security in real time.
- Repeat-clicker shrinkage. Focus on % of users with 2+ failures over a rolling 90 days. Treat it as a coaching flag, not a blame label. Interventions that work: 1:1 micro-coaching, manager follow-ups, and phishing-resistant MFA (FIDO2/passkeys) for those users. Show progress by cohort so improvements are visible.
- Control adoption. Start with % MFA coverage on crown-jewel systems (email/SSO, finance, remote access, admin consoles). Break it down by user segment and by factor type (app/TOTP vs. FIDO2). Add adjacent adoption metrics—% of users with the Report Phish add-in, DMARC policy = reject, SSO coverage—to show that behaviour change is reinforced by controls.
- Tell a risk story, not a vanity story. Combine the signals into a simple resilience index: weight PPR (lower is better), report-rate (higher is better), time-to-report (lower is better), and repeat-clickers (lower is better). Share a one-page dashboard with red/amber/green thresholds, 3-month trend lines, and one action per metric. Keep individual data private; share anonymised rollups company-wide and role-level details with managers. Finally, link the metrics to outcomes—blocked wire fraud attempts, real phish reported pre-click, faster incident containment—to show true ROI.
Read More about the 7 Layers of Cybersecurity
How Fusion Cyber Group Can Help
At Fusion Cyber Group, we understand that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility. Our Security Awareness Training programs educate and empower your employees to recognise and respond to cyber threats effectively. We also conduct Phishing Simulation Testing to help your team stay sharp and vigilant against increasingly sophisticated threats.
What makes our program different is the way it fits your business. We tailor modules by role—finance, HR, executives, frontline—and align scenarios to the tools you actually use (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, QuickBooks). Training is delivered in short, engaging bursts, with bilingual (EN/FR) options and Canadian-hosted platforms where required. When someone clicks a simulation, they receive instant, just-in-time coaching, and your leaders see real metrics—phish-prone rate, report-rate, and time-to-report—on a simple dashboard.
We also deploy a one-click “Report Phish” button and plug reported messages into our 24/7 SOC and MDR pipeline so detections improve continuously. As an MSSP, we can pair awareness with protective controls—email security, DNS filtering, MFA hardening—so behavior change and technology reinforce each other. Fully onboarded clients benefit from our financially backed Cybersecurity Guarantee, underscoring our alignment with your outcomes.
Conclusion
The human element plays a critical role in cybersecurity. By investing in security awareness training, SMBs can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyberattacks while strengthening compliance under PIPEDA and Law 25. Fusion Cyber Group turns training into measurable risk reduction—faster reporting, fewer incidents, lower breach costs—by combining people, process, and always-on monitoring. For leaders, the formula is simple: set a monthly cadence, reward fast reporting, and pair awareness with MFA, email security, and phishing-resistant sign-ins. We provide bilingual delivery, audit-ready records, and a 90-day rollout that fits your calendar—so culture shifts quickly and evidence of improvement is clear to auditors and insurers.
Turn people into a security layer. Talk with a Fusion Cyber advisor about practical options, budget ranges, and compliance considerations.
👉 Get clarity on timelines and what “good” looks like for your team.
Featured links:
Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report
OPC (PIPEDA) training tools and compliance guidance
FAQ:
Isn’t awareness training just “check-the-box”?
Not if you measure report-rate and time-to-report and pair it with phishing simulations and MFA. That’s where risk reduction shows up (and where DBIR says most breaches still begin).
How often should we train?
Monthly micro-modules (10–12 minutes) plus quarterly live refreshers strike the balance for SMBs.
Do simulations hurt morale?
Not when you reward reporters and coach clickers. Make it safe to learn.
Will this satisfy PIPEDA/Law 25 reviewers?
Training + records + policies demonstrate reasonable safeguards and accountability. Add role-based privacy content and keep attendance logs.
What’s the single highest-ROI control to pair with training?
MFA on email/SSO and finance tools; it blocks many phish-to-account-takeover chains.
SITUATION
Canadian SMBs run lean and rely on email, SaaS, and hybrid work.
COMPLICATION
Threat actors weaponize psychology: phishing, pretexting, deepfakes, because people are the easiest path in.
QUESTION
How do you reduce people-driven risk without slowing the business?
ANSWER
Build a light-lift, high-impact awareness program with monthly touchpoints, realistic simulations, and clear reporting rules, then measure it.
Our Cybersecurity Guarantee
“At Fusion Cyber Group, we align our interests with yours.“
Unlike many providers who profit from lengthy, expensive breach clean-ups, our goal is simple: stop threats before they start and stand with you if one ever gets through.
That’s why we offer a cybersecurity guarantee: in the very unlikely event that a breach gets through our multi-layered, 24/7 monitored defenses, we will handle all:
threat containment,
incident response,
remediation,
eradication,
and business recovery—at no cost to you.
Ready to strengthen your cybersecurity defenses? Contact us today for your FREE network assessment and take the first step towards safeguarding your business from cyber threats!